
Table of Contents
Many business owners consider selling their business when they feel ready to move on to new opportunities such as exploring new ventures or industries. Moreover selling may also be a way to join forces with a larger organization, gaining access to greater resources and market reach. In some cases, owners may choose to sell to ensure the company continues to grow under new leadership.
However, selling a business is a complex process that requires careful planning and time. Many owners underestimate the effort needed to prepare for a sale, which can lead to undervaluation or missed opportunities. This guide provides a clear how to sell a business with a step-by-step approach to help you navigate the process.
Preparing to sell your business
If you’re wondering, “I want to selling my business” proper preparation is key to ensuring a smooth transition. Here’s how you can get ready to sell your small business and secure the best deal.
Identifying reasons to sell your business
Before selling your business, it is essential to clearly define your reasons for doing it. A well-thought-out purpose helps you stay focused throughout the process and reassures potential buyers of the business’s value and long-term stability.
Many business owners sell for strategic or personal reasons, such as:
- Retirement
- Exploring new opportunities
- Maximizing business value
- Merging or expanding
- Changes in personal circumstances
Besides that, there are some owners who sell due to financial struggles, this can make attracting buyers more difficult. So if financial issues are a concern, improving performance before listing the business can enhance its value.
Understanding your business’s value
Determining your business’s value is essential to setting a fair and competitive price. An inaccurate valuation can lead to pricing the business too high, discouraging buyers, or too low, resulting in financial loss. Several common assessment methods can help establish an accurate estimate:
- Asset-based valuation by subtracting liabilities from total assets, is ideal for asset-heavy businesses.
- Earnings multiplier approach on annual earnings to estimate future profitability.
- Market value approach by comparing recent sales of similar businesses to determine a competitive price.
- The Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) forecasts future earnings and adjusts them to their present value, making it ideal for businesses with growth potential.
Additionally, maintaining accurate financial records, including tax returns and cash flow statements, is essential in supporting a credible review. A well-documented financial history reassures buyers and strengthens your position during negotiations.
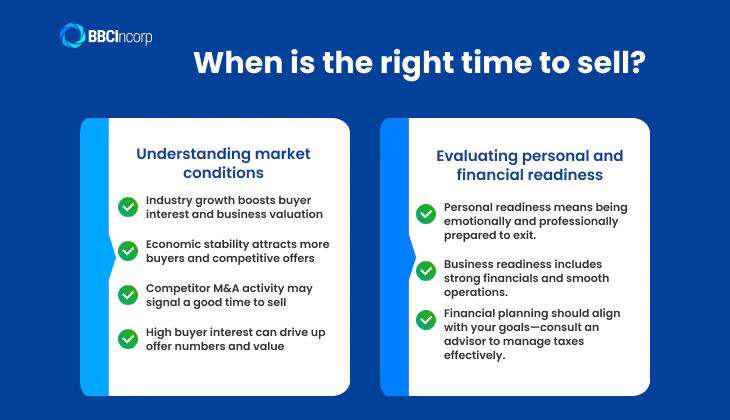
When is the right time to sell?
Selling business at the right moment can maximize value, while poor timing may lead to undervaluation or difficulty finding buyers. So, choosing the right time to sell a business requires careful evaluation of market conditions and personal readiness. To make an informed decision, consider both market conditions and your personal financial readiness.
Understanding market conditions
- Industry growth can influence buyers’ ambitions, making them more inclined to invest. Selling during a period of growth may result in higher business valuations.
- Economic stability often means more potential buyers and competitive offers, while downturns may make financing harder for buyers.
- Competitor activities are merging or acquiring businesses, this could signal an opportunity to sell at a premium.
- Higher interest from potential buyers, such as investors or acquiring businesses, can drive up the number of competitive offers.
Evaluating personal and financial readiness
- Business preparedness means having a well-organized, profitable company with strong financial records, which makes it more appealing to potential buyers.
- Personal transition ensures you are emotionally and professionally ready to step away and that the business can operate without your involvement.
- Financial goals and tax implications should align with your long-term financial plans. Consulting a financial advisor can help you minimize tax liabilities.
Getting your business ready for sale
Preparing to sell your business is essential to attracting buyers and maximizing its value. A well-prepared business appears more stable, profitable, and easy to transition. This process involves strengthening financial performance, optimizing operations, and ensuring legal compliance. So, you should focus on these factors below.
- Improving financial health by maintaining clear and accurate fiscal records, demonstrating consistent revenue growth, managing costs effectively, and reducing outstanding debt can enhance valuation. It provides transparency and helps buyers assess the company’s profitability.
- Streamlining operations with efficient processes makes it easier to transition and manage. Optimizing workflows, automating repetitive tasks, and integrating modern technology can improve productivity and scalability, resulting in the business becomes more attractive to potential buyers.
- Addressing legal issues aligning with industry regulations, resolving any pending legal disputes, and securing intellectual property rights prevent complications during negotiations. Well-documented contracts, licenses, and ownership rights not only add credibility but also reduce risks for both sellers and buyers.
Best way to selling a business
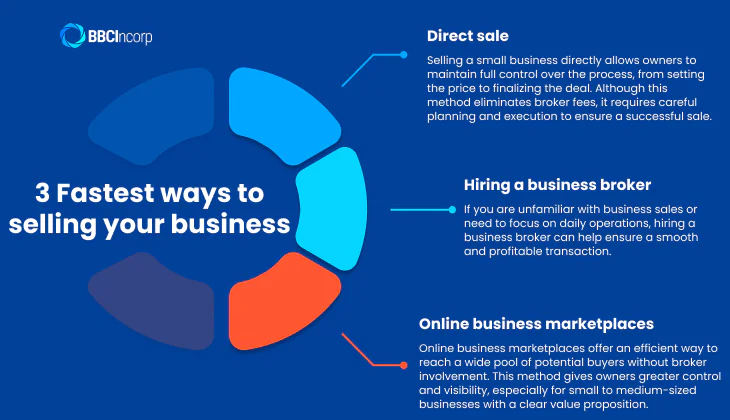
It is important to identify the ways to sell a business that match your goals. Understanding how to sell your business with the right approach can help you make informed decisions and secure the best possible deal.
Direct sale
Selling a small business directly allows owners to maintain full control over the process, from setting the price to finalizing the deal. Although this method eliminates broker fees, it requires careful planning and execution to ensure a successful sale. The process typically involves:
- Preparing financial records: Include a fair market valuation, resolve any legal or operational issues, and present clear financials to boost buyer confidence and negotiation efficiency.
- Marketing the sale: Use industry networks, online marketplaces, and direct outreach. Create a compelling sales pitch and use confidentiality agreements to protect sensitive information.
- Negotiating with buyers: Engage multiple buyers to improve deal terms. Verify their financial capability and ensure that the final agreement supports the business’s long-term value.
- Completing legal procedures: Draft sale agreements, conduct due diligence, and confirm payment before transferring ownership. Consider hiring legal and financial advisors to minimize risks and ensure compliance.
Hiring a business broker
For many business owners, selling a business is a complex process that requires industry knowledge, negotiation skills, and significant time investment. If you are unfamiliar with business sales or need to focus on daily operations, hiring a business broker can help ensure a smooth and profitable transaction. This way contains these key stages:
- Selecting a broker: Choose a broker with proven experience in your industry, a strong reputation, and a transparent fee structure to avoid unexpected costs later.
- Valuing the business: Evaluate your financials, assets, and current market trends to determine a fair and competitive asking price.
- Marketing the business: Leverage the broker’s network to discreetly promote your business while maintaining confidentiality.
- Negotiating the terms: Work with the broker to address buyer concerns, structure favorable deals, and maximize your final sale price.
- Closing the sale: Finalize the transaction through due diligence, legal paperwork, and transition planning to reduce risks and ensure a smooth handover.
Online business marketplaces
Online business marketplaces offer an efficient way to reach a wide pool of potential buyers without broker involvement. This method gives owners greater control and visibility, especially for small to medium-sized businesses with a clear value proposition.
However, it also requires significant effort to manage inquiries, negotiations, and due diligence independently. The process in this approach includes:
- Selecting a suitable platform: Choose platforms tailored to your industry and business size. Websites like BizBuySell, Flippa, or Exchange Marketplace offer features such as confidentiality tools and sector-specific support.
- Creating a comprehensive listing: Include detailed information on financials, operations, assets, and growth potential. Enhance the listing with high-quality visuals and a compelling business summary to attract serious buyers.
- Managing buyer inquiries: Respond promptly to interested parties, provide essential documentation, and assess buyer credibility before entering into formal negotiations.
- Negotiating and closing the deal: Once a serious offer is received, negotiate favorable terms, draft legal agreements, and complete due diligence to ensure a smooth and secure transition.
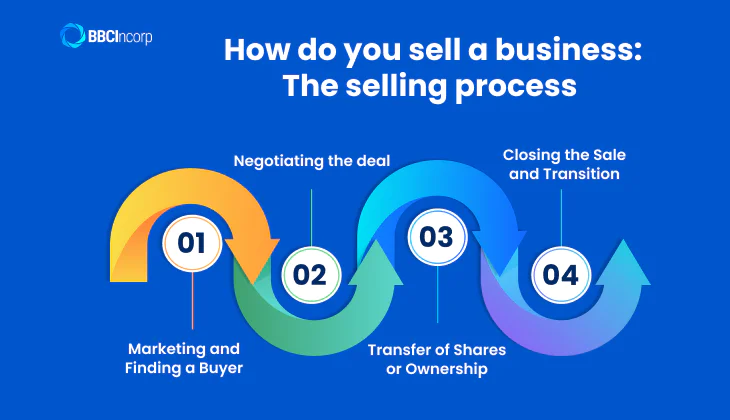
How do you sell a business: The selling process
Knowing the process of selling a business is key to achieving a quick and successful sale. Let’s explore how to sell a business fast, enabling you to navigate each stage with confidence and ensuring a smooth transition. Here’s an overview of the key steps involved.
Step 1: Marketing and Finding a Buyer
A well-executed marketing strategy can significantly increase the chances of finding the right buyer for your company. The key is to highlight the strengths and opportunities your business offers, such as its customer base, profitability, unique market position, or proprietary technology.
Moreover, providing key financial information, such as revenue trends, profit margins, and assets, is essential for building credibility and attracting serious buyers.
When it comes to identifying potential buyers, there are several categories to consider:
- Strategic buyers who are looking to expand their market share or gain access to new products, services, or technologies in the same industry as yours.
- Financial buyers are private equity firms and investors fall into this category. They are primarily interested in the financial return on investment and may focus on companies with growth potential.
- Individual buyers searching to own and operate a small business may be attracted to a company with a solid foundation and growth opportunities.
If you need help selling your business quickly, online marketplaces can provide valuable resources and connect you with potential buyers. For those wondering how to sell your business online, seeking assistance from specialized service providers can streamline the process and increase your chances of success.
Step 2: Negotiating the deal
It’s crucial to manage the due diligence process effectively before finalizing the purchase agreement. During this stage, you should focus on the essential factors:
- Price reflects your business’s market value and growth potential.
- Payment structure clearly determines whether the buyer is offering an all-cash deal or if there will be payments over time, such as through earn-outs or installment plans.
- Closing date that works for both parties, ensuring sufficient time for the due diligence process and finalizing the agreement.
Step 3: Transfer of Shares or Ownership
When the deal is accepted by both parties, the next step is the transfer of equity or ownership rights. This stage is vital as it involves the legal and administrative processes of officially handing over the business to the buyer. Here’s what this typically involves:
- Preparing and signing transfer documents such as stock certificates (for a share sale) or membership interest assignments (for an LLC).
- Updating company records including the shareholder registry or operating agreement to express the new ownership structure.
- Fulfilling legal requirements consists of notifying relevant authorities or updating business licenses and permits to reflect the new holder.
Step 4: Closing the Sale and Transition
At this stage, you finalize all legal and financial documents to complete the sale. This consists of reviewing the purchase agreement and ensuring all terms and obligations are met by both parties. Any conditions outlined in the agreement must be fulfilled before the transaction can proceed. And when closing the sale, focus on these essential tasks:
- Signed legal documentation such as the bill of sale, asset purchase agreement, and non-compete agreements, to officially transfer ownership and assets to the buyer.
- Resolve financial obligations by clearing any outstanding debts, taxes, or financial liabilities. This may also involve confirming the buyer’s financing arrangements if applicable.
Once the documents are signed and all obligations are met, the business is officially transferred, and the new owner can take control. Ensuring a seamless transition is critical for the ongoing success of the business under new ownership. Proper communication and thorough preparation are key during this stage.
Legal and financial considerations for selling your business
When selling your business, taking care of legal requirements and financial aspects helps ensure compliance, reduce risks, and maximize the value of your sale.
Legal documents
When selling a business, having the right legal documents in place is essential to ensure a smooth and legally binding transaction. These documents serve to formalize the sale, outline the terms and conditions, and protect both parties involved. Therefore, you should pay attention to key documents such as the Bill of Sale, Asset Purchase Agreement, Noncompete Agreement, and others.
Tax implication of the sale
The sale may be taxed as either a capital gain or ordinary income, depending on how the deal is structured. For example, selling equipment may trigger depreciation recapture, which is taxed as ordinary income. In contrast, a share sale usually results in capital gains tax, often with lower rates. You must also consider Value Added Tax (VAT) or Corporate Income Tax (CIT) obligations, depending on your country’s laws.
Post-sale considerations
Once a business sale is completed, you still have important responsibilities to address for ensuring legal compliance and financial clarity. The seller may need to fulfill obligations outlined in the sale contract, such as honoring a non-compete agreement or assisting with the business handover.
On the financial side, it’s important to calculate and pay any taxes arising from the sale, like capital gains tax, and to settle remaining debts or employee entitlements.
If you’re considering a more flexible and private business structure, the Delaware Close Corporation might be an ideal choice. It allows you to bypass certain corporate formalities, such as annual meetings and provides tax flexibility between C Corporation and S Corporation status.
While it’s ideal for smaller, closely-held businesses, it may not be suitable for those seeking significant outside investment in the future.
Conclusion
This article has clarified how to sell a business by emphasizing the importance of planning, clear communication, and proper legal and financial management. With thoughtful preparation and expert guidance, you can navigate the process smoothly and secure the best possible deal when selling your small business.
Additionally, involving professionals such as lawyers or financial advisors can help you avoid costly mistakes and ensure compliance with applicable laws. For personalized assistance at every stage, consider reaching out to BBCIncorp.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you sell a business quickly?
To expedite the sale of your business, prioritize enhancing financial transparency, optimizing operational efficiency, and setting a competitive price.
What documents do I need when selling a company?
Before transferring ownership, it is essential to gather all necessary paperwork, including up-to-date financial statements, tax records, legal documentation, an inventory of assets, and a formal sales agreement.
How do I sell a business that is struggling financially?
If your business is struggling with debt or declining performance, consider working with a financial recovery advisor. They can help assess the situation, propose a turnaround plan, and explore legal protections under the Bankruptcy and Insolvency Act to keep the business running.
If recovery is not feasible, selling the business either partially or entirely may be the best option. A trustee can support you in finding buyers, negotiating fair terms, and maintaining operations during the process.
Disclaimer: While BBCIncorp strives to make the information on this website as timely and accurate as possible, the information itself is for reference purposes only. You should not substitute the information provided in this article for competent legal advice. Feel free to contact BBCIncorp’s customer services for advice on your specific cases.
Industry News & Insights
Get helpful tips and info from our newsletter!
Stay in the know and be empowered with our strategic how-tos, resources, and guidelines.





