
Table of Contents
A Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) is a unique number assigned by the IRS to individuals and businesses for tax reporting purposes. It is essential to ensure that tax obligations are accurately tracked, particularly when starting a business, filing tax returns, or managing employee payroll.
Knowing how to get a tax ID is important for both entrepreneurs and individuals to comply with tax regulations. While the process may seem complex at first, it becomes much easier once you understand the available options and the requirements for obtaining one. In this article, we’ll guide you through the steps to apply for a Tax ID efficiently and correctly, helping you stay compliant and avoid delays.
What is a TIN?
A TIN is a unique identification number used by the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to track individuals, businesses, and other entities for tax purposes. It is essential for submitting tax returns and maintaining compliance with federal tax regulations. This number allows the IRS to accurately process returns and monitor related financial activities.

So, what is a taxpayer ID? It refers to the same concept and ensures the smooth handling of income reporting and other tax-related matters. Depending on whether you are an individual or a business, the required type of TIN may vary.
When applying for a tax ID, it’s important to understand the difference between TIN vs EIN. While both are tax identification numbers, they serve different purposes depending on whether you’re filing as an individual or running a business.
Who needs a TIN?
- For Individuals: U.S. citizens and authorized residents use a Social Security Number (SSN) to file taxes and report income. While non-U.S. residents who are not eligible for an SSN but need to file U.S. taxes are issued an ITIN.
- For businesses: Corporations, partnerships, and LLCs need an Employer Identification Number (EIN) for tax reporting, especially if they have employees. This number is also required for opening business accounts and applying for licenses. Sole proprietors or LLCs may use their SSNs in place of an EIN in some cases, but an EIN is typically recommended.
Types of TINs
There are several forms of tax identification numbers (TINs), each designed for specific parties. Understanding these different types is crucial for proper tax filing and ensuring compliance.
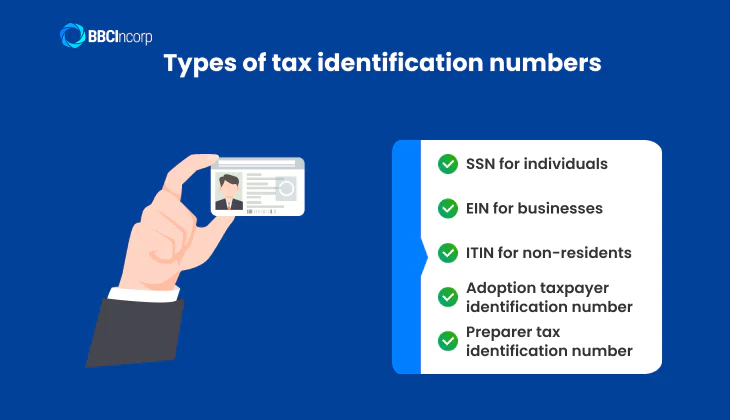
SSN (Social Security Number) for individuals
A SSN is a distinct identification number assigned by the U.S. Social Security Administration (SSA) to individuals. It is primarily used for filing taxes, tracking earnings, and ensuring proper social security benefits. U.S. citizens and authorized residents typically receive their SSNs at birth or upon work authorization.
Sole proprietors and LLCs may use their SSNs instead of an EIN for business tax filings. Additionally, businesses must collect SSNs from employees and independent contractors for tax reporting, such as issuing 1099-NEC forms.
EIN (Employer Identification Number) for businesses
An EIN is a federal tax identifier number issued by the IRS to identify a business entity. It is essential for corporations, LLCs, partnerships, and nonprofit organizations when filing taxes, opening bank accounts, hiring employees, and managing payroll. If you’re wondering what is a business tax ID number, the EIN is the most common answer.
Even sole proprietors may need an EIN if they hire workers or form a partnership or corporation. Obtaining an EIN is free and can be done online through the IRS website or by mail or fax. The application process is straightforward and typically quick.
ITIN (Individual Taxpayer Identification Number) for non-residents
An ITIN is a nine-digit tax identification number issued by the IRS to individuals who are not eligible for a SSN but are still required to file a U.S. tax return. It is used exclusively for federal tax reporting purposes and does not authorize employment or provide access to Social Security benefits.
This number is commonly assigned to non-U.S. citizens who have U.S. tax obligations, such as foreign investors, non-resident independent contractors, scholarship recipients, or dependents and spouses of taxpayers.
Even without residing in the United States, these individuals may still need to report income or claim certain tax benefits, including dependent tax credits or exemptions under international tax treaties.
Adoption taxpayer identification number
An ATIN is a temporary identification number assigned by the IRS for children who are in the process of being adopted in the United States. It is used primarily for tax filing purposes, especially when claiming the adoption tax credit or other adoption-related tax benefits.
Adoptive parents who do not yet SSN for the child can apply for an ATIN to file tax returns. The ATIN is only valid until the child receives an SSN. It ensures that adoptive families can claim tax benefits without delays during the adoption process.
Preparer tax identification number
A Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN) is a unique number that all paid tax preparers must use when filing U.S. federal tax returns or claims for refunds with the IRS. This number is issued to professionals such as accountants, tax advisors, and others who assist clients with their tax filings.
The PTIN helps the IRS identify who prepared each tax return. Unlike other tax identification numbers, PTINs must be renewed annually. Tax preparers can apply for a PTIN easily through the IRS website or by mail.
What is a Tax ID used for?
A Tax ID helps track individuals and businesses for tax purposes. It plays a vital role in ensuring accurate tax reporting and compliance with U.S. tax laws.
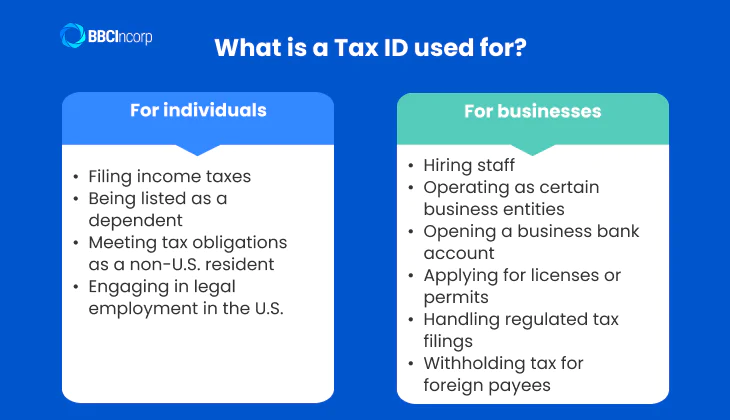
For individuals
- Filing income taxes: U.S. citizens, permanent residents, and people authorized to work must have an SSN to report their income to the IRS through annual tax returns.
- Being listed as a dependent: To be claimed on someone else’s tax return such as a parent’s you must have either an SSN or an ITIN so the IRS can verify and approve related tax credits.
- Meeting tax obligations as a non-U.S. resident: Individuals who are not eligible for an SSN but earn U.S.-sourced income, like foreign investors or scholars, use an ITIN to file tax returns and claim eligible deductions or exemptions.
- Engaging in legal employment in the U.S.: An SSN is required by employers to report your earnings and handle Social Security contributions on your behalf.
For businesses
- Hiring staff: An EIN is mandatory to report employee wages, file payroll taxes, and comply with employment tax regulations.
- Operating as certain business entities: Corporations, partnerships, and multi-member LLCs are required to use an EIN for tax filings and official records.
- Opening a business bank account: Financial institutions usually require an EIN to verify the business’s legal status before approving account applications.
- Applying for licenses or permits: Many local and state governments request an EIN during the licensing process to ensure the business is properly registered.
- Handling regulated tax filings: Businesses involved in activities like selling alcohol, tobacco, or fuel must use an EIN when submitting specific excise tax returns.
- Withholding tax for foreign payees: When paying non-resident individuals or entities, businesses need to withhold a portion of the payment for taxes and report it using their EIN.
How to obtain a taxpayer identification number?
The application process varies depending on the specific type of TIN required. If you’re wondering how to get a taxpayer ID, below are the steps to apply for each of the 3 common TINs.
Social Security Number (SSN)
Before starting your application, ensure that you are eligible for an SSN. Typically, this means you must have a job offer or be authorized to work in the U.S. International students (F-1 or J-1 visa holders) must meet specific employment and enrollment requirements.
Then, you visit the Social Security Administration (SSA) website and finish the Online SSN Application. Once submitted, save your confirmation number for use during your appointment. After that, use the SSA Office Locator to find your nearest Social Security office, then make an appointment online or by phone and bring all required original documents along with your confirmation number to proceed.
- Valid passport
- Most recent I-94 (Arrival/Departure Record)
- I-20 form (for F-1 visa holders) or DS-2019 (for J-1 visa holders)
- Official job offer letter from your U.S. employer
- SSN support letter (if issued by your school or program sponsor)
- Additional photo ID (e.g., student ID card or driver’s license)
EIN (Employer Identification Number)
To apply for an EIN, you must submit IRS Form SS-4, which collects essential information about your business and the responsible party who manages or controls the entity. The application is free and can be submitted through several methods, depending on your location and preference.
- Apply online (U.S. only): This is the fastest method and is available to businesses whose principal office is in the U.S. or a U.S. territory. You visit the IRS application page https://www.irs.gov/, complete the form, and receive your EIN immediately after validation.
- Apply by Fax: Download and complete Form SS-4, then fax it to the appropriate number listed on the IRS website. If you provide a return fax number, the IRS will send your EIN within approximately 4 business days.
- Apply by Mail: Send the completed Form SS-4 to the address specified for your location on the IRS website. The result typically takes up to 4 weeks.
- Apply by Phone (International Applicants): Call +1-267-941-1099 (not toll-free) from Monday to Friday, 6 a.m. to 11 p.m. (ET). Besides that, you must be authorized to receive the EIN and answer questions about the application.
Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN)
To apply for an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN), you may submit your application by mail, through a Certifying Acceptance Agent (CAA), at a VITA site offering ITIN services, or in person at an IRS Taxpayer Assistance Center. Processing may take up to 11 weeks, particularly during peak tax season or for applicants outside the United States.
Before applying, prepare the following documents and information:
- Completed Form W-7
- A federal income tax return (unless exempt)
- Original or certified copies of identity and foreign status documents (such as a passport)
- Proof of U.S. residency for dependents, if applicable (e.g., school or medical records)
- Current mailing address
- Details of your chosen submission method (mail or in-person)
*Notices after applying for an ITIN:
- CP565: ITIN has been assigned. No further action is required.
- CP566: Additional information is needed to complete the processing of your application.
- CP567: Your application was rejected. You will need to resubmit it.
Other types of TINs
Adoption Taxpayer Identification Number (ATIN)
To apply for an Adoption Taxpayer Identification Number (ATIN), you should complete Form W-7A at least 4 to 8 weeks before the ATIN is needed. Ensure the form is properly signed and dated, and mail it to the IRS address listed under the “Where To File” section. Don’t forget to include all required supporting documents.
You must attach proof must be signed and dated that the child has been legally placed with you for adoption, not foster care. Acceptable forms of proof include:
- A copy of the placement agreement from an authorized adoption agency
- A hospital release document signed by an official, allowing a newborn to be placed with you
- A court order approving the child’s placement in your home for legal adoption
- An affidavit from an adoption attorney or government official confirming the placement under state law
If the child being adopted is from another country and is a U.S. citizen or resident alien, you must include a copy of one of the following:
- The child’s permanent resident card (green card)
- Certificate of Citizenship
- Passport bearing the “I-551” stamp
Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN)
To apply for a Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN), you must first create an account on the IRS PTIN system using your name and email address. After receiving a temporary password, log in to complete the application. You’ll need to pay a non-refundable fee of $19.75 via credit/debit card or eCheck. Once submitted, your PTIN will be issued online.
Before applying, prepare the following documents and information:
- Social Security number
- Personal details (name, date of birth, mailing address)
- Business details (name, address, phone number)
- The previous year’s individual tax return
- Explanation for any felony convictions (if applicable)
- Description for tax compliance issues (if applicable)
- Credit/debit/ATM card or eCheck for the application fee
- U.S.-based professional certification details (e.g., CPA, attorney), if available
Where do you find your tax ID number?
Your Tax ID number is essential for filing taxes, opening bank accounts, and handling official paperwork. So, how to find my tax identification number? It depends on whether you’re an individual or a business, your Tax ID can be found in different documents.
For Individuals (SSN)
Your Social Security Number can typically be found on:
- Your Social Security card
- Previously filed tax returns (e.g., Form 1040)
- W-2 forms issued by your employer
- Official documents from banks, insurance providers, or government agencies
For Businesses (EIN)
Your Employer Identification Number may appear on:
- The IRS confirmation letter (CP 575) you received when the EIN was assigned
- Business tax returns (e.g., Form 1120 for corporations, Form 1065 for partnerships)
- Business bank account statements or account documents
- Business loan applications or approval letters
- State or local business licenses and permits
Note
If you cannot find your EIN through these sources, contact the IRS Business and Specialty Tax Line at 800-829-4933. Be prepared to verify your identity and provide details about your business. This step ensures that the IRS can securely confirm your EIN.
Obtain your TIN with BBCIncorp
Getting a TIN is essential for managing taxes and staying compliant with government regulations. If you’re unsure how to obtain a tax ID number, BBCIncorp offers straightforward, professional support to help you complete this process efficiently, whether you’re in the U.S. or Belize.
EIN application in Delaware (US)
For businesses in the U.S., particularly those incorporated in Delaware, BBCIncorp provides dedicated EIN application services in Delaware. This Employer Identification Number (EIN) is essential for opening a business bank account, filing taxes, and hiring employees. BBCIncorp’s team ensures your EIN application is filed correctly with the IRS, minimizing delays and rejections.
TIN registration in Belize
In Belize, companies must also register for a TIN with the Belize Tax Service. This number is mandatory for submitting annual tax filings and meeting local tax compliance requirements. BBCIncorp includes TIN registration as part of our Belize company formation packages, or it can be purchased as a stand-alone service.
Conclusion
Obtaining a TIN is an essential step for both individuals and businesses looking to operate legally and efficiently within the United States. It serves as a critical tool for tax reporting, financial transactions, and interactions with the Internal Revenue Service.
More importantly, having a valid TIN ensures compliance with federal tax regulations, helping to prevent potential legal and administrative issues. Understanding how to get a tax ID is not merely a procedural task but a necessary foundation for long-term financial and operational success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use my SSN for my business?
Yes, but it’s limited. Sole proprietors without employees can use their SSN for business taxes. However, for hiring employees, forming an LLC, corporation, or partnership, an EIN is required.
What happens if I lose my TIN?
If you lose your TIN, you can retrieve it by contacting the issuing authority. For a SSN, submit Form SS-5 to the Social Security Administration, and if it’s an EIN, refer to your previous tax documents or contact the IRS for assistance.
Do I need a new TIN if I change my business structure?
Yes, you typically need a new TIN if your business structure changes, such as switching from a sole proprietorship to a corporation or partnership. However, minor changes like updating your business name usually do not require a new TIN. Always check IRS guidelines to confirm your specific case.
Disclaimer: While BBCIncorp strives to make the information on this website as timely and accurate as possible, the information itself is for reference purposes only. You should not substitute the information provided in this article for competent legal advice. Feel free to contact BBCIncorp’s customer services for advice on your specific cases.
Industry News & Insights
Get helpful tips and info from our newsletter!
Stay in the know and be empowered with our strategic how-tos, resources, and guidelines.





