
Table of Contents
A tax service business provides professional help with preparing, filing, and advising on tax matters for individuals and businesses. Services can range from basic tax returns to strategic tax planning and IRS representation, depending on the preparer’s credentials.
In the U.S., demand for tax preparation remains high, with the market expected to grow from $32.33 billion in 2024 to $34.06 billion in 2025(1). This growth is driven by complex tax laws and the need for expert guidance. For entrepreneurs, it’s a profitable opportunity—whether starting from home or expanding into an office.
This guide covers everything you need to know how to start a tax preparation business—from setup and certifications to marketing and scaling. If you’re exploring a tax preparation business opportunity or want to understand what a tax business involves, this resource is your step-by-step roadmap.
What is a tax service business and why it’s a smart venture
Looking for a business opportunity that combines low startup costs with high demand? Have you considered the growing need for expert tax preparation services? With constantly changing tax laws and a wide range of starting your own tax preparation business, starting a tax service business could be your path to a profitable and rewarding venture.
What is a tax service business?
The tax preparation business opportunity is appealing due to its high demand, low startup costs, and strong profit potential. With constantly changing tax laws, more people and businesses need expert assistance, making starting a tax business a smart move.

You can start a tax prep business from home easily, keeping overhead low while tapping into a lucrative seasonal market. Beyond tax season, expanding into year-round services like tax consultant business helps maintain steady income and grow your business sustainably.
Why start a tax preparation business?
The tax preparation business opportunity is appealing due to its high demand, low startup costs, and strong profit potential. With constantly changing tax laws, more people and businesses need expert assistance, making starting a tax business a smart move.
You can easily start a tax prep business from home, keeping overhead low while tapping into a lucrative seasonal market. Beyond tax season, expanding into year-round services like tax consulting and bookkeeping helps maintain steady income and grow your business sustainably.
How to start a tax preparation business
Starting a tax preparation business is a smart move given the steady demand and lucrative opportunities in the tax services industry. Whether you’re aiming to work from home or launch a full-scale office, understanding the essential steps is key. Follow the step-to-step guide below to know how to start a tax preparation business.
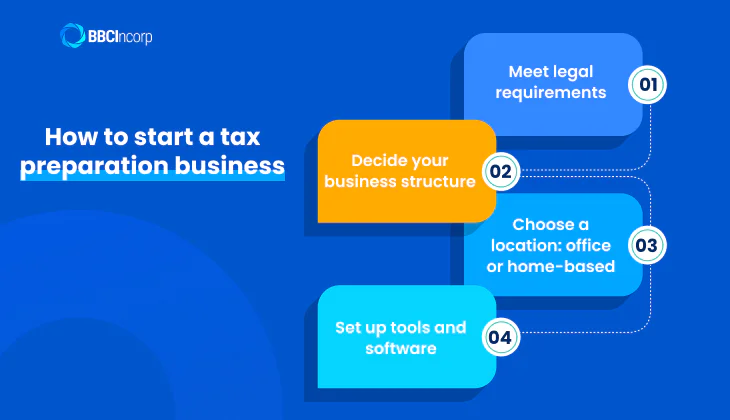
Meet legal requirements
The first step in how to start your own tax business is ensuring you meet all necessary legal requirements. The IRS mandates that all paid tax preparers obtain a Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN), which allows you to legally prepare federal tax returns.
Additionally, if you plan to electronically file tax returns, you must secure an Electronic Filing Identification Number (EFIN) by applying through the IRS e-file program.
Registering your business name with your state is essential for branding and legal operation. Each state may also have its own certification or licensing requirements for tax preparers, so check local regulations thoroughly.
While optional, becoming an IRS Enrolled Agent (EA) can significantly boost your credibility, allowing you to represent clients before the IRS and offer a wider range of tax services.
Understanding what do I need to start a tax preparation business helps set a strong foundation, ensuring compliance and professionalism from the start.
Decide your business structure
How do I start my own tax business? One of the critical decisions involves selecting the appropriate business structure. Common options include sole proprietorship, limited liability company (LLC), and corporation. Each comes with varying implications for liability protection, tax benefits, and setup complexity.
- A sole proprietorship is the simplest to establish and often suitable for solo tax preparers just starting out. However, it offers little personal liability protection.
- An LLC offers more protection and potential tax advantages while maintaining relatively simple administration.
- Corporations provide the strongest liability protection but involve more complex regulations and costs.
After opening a tax business, register it with your state’s business authority and obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS. This process is fundamental to how to open a tax business, as it legitimizes your operation and allows for proper tax reporting.
Choose a location: office or home-based
When figuring out how to start a tax preparation business from home or office, your choice of location is important. A home-based setup offers low overhead costs, making it ideal for solo tax preparers or those testing the waters. It provides flexibility but requires ensuring your workspace is professional and secure.
Alternatively, starting a tax office provides a more formal, professional environment. It can accommodate a growing team and client meetings, enhancing credibility. However, this option comes with higher costs, including rent, utilities, and furnishing.
Whichever you choose, prioritize data privacy and security. A secure client area and proper data handling policies are essential to protect sensitive tax information and comply with IRS regulations.
Set up tools and software
To start tax prep business efficiently, equipping yourself with the right tools and software is non-negotiable. Professional tax software such as Drake, TaxSlayer Pro, UltraTax CS, or Intuit ProConnect streamlines the preparation and filing process while ensuring accuracy and compliance.
Additionally, a secure file-sharing system is crucial to exchange documents safely with clients. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools help manage client communications and appointments, improving organization and client satisfaction. Bookkeeping and accounting software assist in tracking your business finances and maintaining IRS compliance.
When starting a tax preparation business, ensure all digital tools comply with IRS security standards for data protection. Investing in reliable software not only boosts efficiency but also builds trust with your clients.
This comprehensive approach covers how to start my own tax business successfully, from what I need to start a tax preparation business to choosing the right setup and tools. With your operations in place, the next step is building visibility, earning trust, and bringing in clients who will drive your success.
Attracting and growing your client base
Building a strong client base is essential when you start your own tax business. Effective marketing and exceptional service are key to establishing and expanding your tax consultant business.
Market your tax service business
To attract clients when starting your own tax preparation business, focus on a robust online presence and community engagement:
- Professional Website: Develop a user-friendly website that clearly outlines your services, credentials, and contact information.
- Google Business Profile: Claim and optimize your Google Business Profile to enhance local SEO and appear in local search results.
- Social Media and Community Groups: Engage with potential clients by sharing tax tips and updates on platforms like Facebook and LinkedIn.
- Promotions: Offer first-time client discounts or referral incentives to encourage new business and word-of-mouth marketing.
These strategies can significantly boost your visibility and client acquisition efforts.
Deliver excellent client service
Providing outstanding service is crucial for client retention and referrals in your tax preparer business:
- Responsive Communication: Ensure prompt and clear communication to address client inquiries and concerns.
- Flexible Consultations: Offer mobile appointments or virtual consultations to accommodate client preferences.
- Data Security and Transparent Pricing: Build trust by securely handling client data and maintaining transparent pricing structures.
By prioritizing these aspects, you can foster strong client relationships and encourage repeat business.
Implementing these strategies will position your tax preparation business for growth and success in a competitive market.
Managing and scaling your tax service business
Managing and scaling your tax preparation business requires careful financial management and strategic growth planning. Handling your business finances like a pro and expanding your services or team at the right time are essential for long-term success.
Handle financials like a pro
When you start tax business operations, it’s crucial to open a separate business bank account. This separation simplifies tracking income, expenses, and tax obligations, which is vital for both business decisions and IRS compliance.
Using accounting software like QuickBooks or hiring a professional bookkeeper can help you maintain clean, organized financial records. Accurate record-keeping not only supports day-to-day management but also ensures you are prepared during tax season or in case of an audit.
Expand your team or services
Scaling your tax preparation business often means knowing when to hire additional staff. Many tax businesses choose to bring on extra help during the busy tax season to handle increased workload efficiently.
Hiring specialists to offer services such as audits or tax planning can also add value and differentiate your business. Training new employees thoroughly ensures your team remains compliant with IRS regulations and provides consistent quality service.
To grow your revenue streams, consider diversifying your service offerings beyond basic tax preparation. Expanding into areas like business formation assistance, IRS audit support, and year-round tax consulting can help stabilize income throughout the year.
Additionally, offering bilingual services or focusing on niche markets—such as real estate investors, freelancers, or healthcare professionals—can broaden your client base and open new opportunities.
For anyone starting a tax business or wondering how to start a tax preparer business, these financial and operational strategies are key to building a resilient and scalable tax service business that thrives beyond tax season.
Incorporating your tax service business the right way
Incorporating a tax service business can be a daunting task for many entrepreneurs. Many business owners struggle with questions like which entity type to choose and how to meet all regulatory obligations.
For those starting a tax service business from home or looking to scale across multiple states, using a professional incorporation service can save time and reduce stress by handling these details efficiently.
Benefits of incorporating through a professional service
Incorporating your tax preparation business offers numerous advantages, including:
- Time and compliance efficiency: Professional services streamline the incorporation process, ensuring adherence to state or offshore regulations, which is especially beneficial for entrepreneurs starting a tax service business from home or expanding across states.
- Elimination of guesswork: Expert assistance removes uncertainties when registering your business entity, allowing you to focus on core operations.
- Tax advantages: Incorporation can provide tax benefits such as deductions on business expenses and potential deferment of net operating losses, enhancing your tax consultant business’s financial health
How BBCIncorp simplifies the process
BBCIncorp offers comprehensive company formation services that simplify the incorporation process for your tax service business:
- Global coverage: Incorporation support in the U.S., Belize, BVI, Hong Kong, and more—ideal for entrepreneurs looking to scale or operate across borders.
- End-to-end services: From document filing and registered agent provision to bank account setup support, BBCIncorp handles all aspects of incorporation.
- Expert support: Access to local experts who guide you through each step, ensuring a smooth and compliant incorporation process.

By leveraging BBCIncorp’s services, you can efficiently incorporate your tax preparation business, positioning it for growth and success in the competitive market. Learn more about how to form your tax service business entity with BBCIncorp company formation services.
Conclusion
Starting a successful tax service business involves key steps such as meeting legal requirements, choosing the right business structure, setting up your location and tools, and focusing on client growth and financial management. Understanding how to start a tax preparation business is essential to laying the groundwork for long-term success in this in-demand industry.
By following these guidelines, you can build a strong foundation for long-term success in this in-demand industry. With dedication and excellent service, you’ll gain valuable experience and client trust that will fuel your business’s growth over time.
Ready to start? Incorporate your tax service business the right way with BBCIncorp’s expert company formation services. Launch confidently and focus on growing your business today.
*Reference:
(1) https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/tax-preparation-services-global-market-report
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need to register my tax business with the IRS?
Yes, if you’re operating a tax preparation business in the U.S., you must register with the IRS. All paid tax return preparers are required to obtain a Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN) before preparing or assisting in preparing federal tax returns for compensation. This registration helps the IRS track and regulate tax preparers.
Can I run a tax business from home, or do I need a physical office?
You can operate your tax service business from home, provided you meet certain IRS criteria for a home office deduction. To qualify, the space must be used exclusively and regularly for business activities, and it should be your principal place of business.
If you meet these requirements, you may be eligible to deduct expenses related to the business use of your home.
What are the busiest times of year for tax preparers?
The peak season for tax preparers typically spans from January through April, coinciding with the U.S. tax filing deadline on April 15. During this period, preparers experience a significant increase in workload due to the high volume of tax returns.
Some preparers also see increased activity in the fall, particularly in September and October, as clients seek assistance with extensions and year-end planning.
Do I need to renew my certifications or registrations every year?
Yes, certain certifications and registrations require annual renewal:
- PTIN: All paid tax preparers must renew their PTIN annually between October 16 and December 31. The renewal process is completed online through the IRS website.
- Enrolled Agent (EA): If you’re an EA, you must complete 72 hours of continuing professional education (CPE) every three years, including two hours of ethics or professional conduct each year. Additionally, you need to file Form 8554 to renew your enrollment.
- Annual Filing Season Program (AFSP): This voluntary program requires tax preparers to complete continuing education courses annually to receive a Record of Completion. While not mandatory, participation can enhance your professional standing.
Disclaimer: While BBCIncorp strives to make the information on this website as timely and accurate as possible, the information itself is for reference purposes only. You should not substitute the information provided in this article for competent legal advice. Feel free to contact BBCIncorp’s customer services for advice on your specific cases.
Industry News & Insights
Get helpful tips and info from our newsletter!
Stay in the know and be empowered with our strategic how-tos, resources, and guidelines.





